The three most important performance measures of an operation:
- Flow rate, also known as the through put – flow units going through the process per unit of time. The minimum between demand rate and process capacity. It captures the flow, meaning it captures how much work a resource is currently doing.
- Inventory – number of flow units in the process at any given amount of time
- Flow time – the time it take the flow unit to go through the process from beginning to end
Some PROCESS ANALYSIS Definitions
These calculations and definitions help to determine the flow rate of the process without actually observing the process in action.
FLOW UNIT – the atomic unit of analysis. e.g. Flow of customers, flow of product, flow of money
Inventory happens whenever hear of mismatches between supply and demand.
BOTTLENECK – process step with the lowest capacity
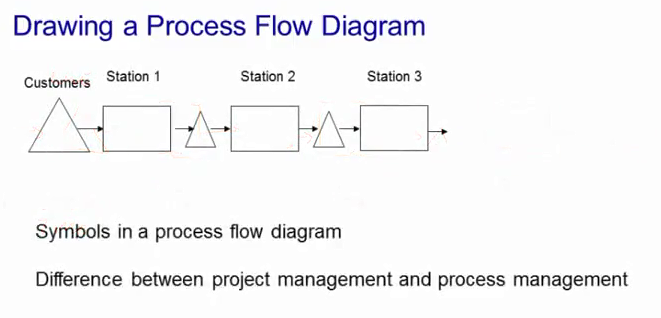
Process Flow Diagrams – maps describing how the flow units goes from being an input into the process, just from leaving the process as a finished unit of output.
Process Management is all about doing things repeatedly.
Processing Time or Activity Time – always expressed in units of time for flow unit, captures how long a resource takes to serve a flow unit. E.g. How long a worker spend on a task?
Capacity = 1/processing time – how many units can the worker make per unit of time. If there are M workers at the activity, capacity=m/processing time. It measures how much work the resource could be doing if it worked all out.
Process Capacity – capacity of the bottleneck
Utilization = Flow Rate/Capacity – ratio between the flow rate and the capacity.